Introduction
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way your body processes blood sugar (glucose). It is the most common form of diabetes, impacting millions of people worldwide. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disease, type 2 diabetes is often linked to lifestyle factors and genetics. You can also try Metformin hcl 500 mg from dose pharmacy to treat Type 2 diabetes. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors can help in early detection and effective management.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. When this process is disrupted, excess glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to various health complications.
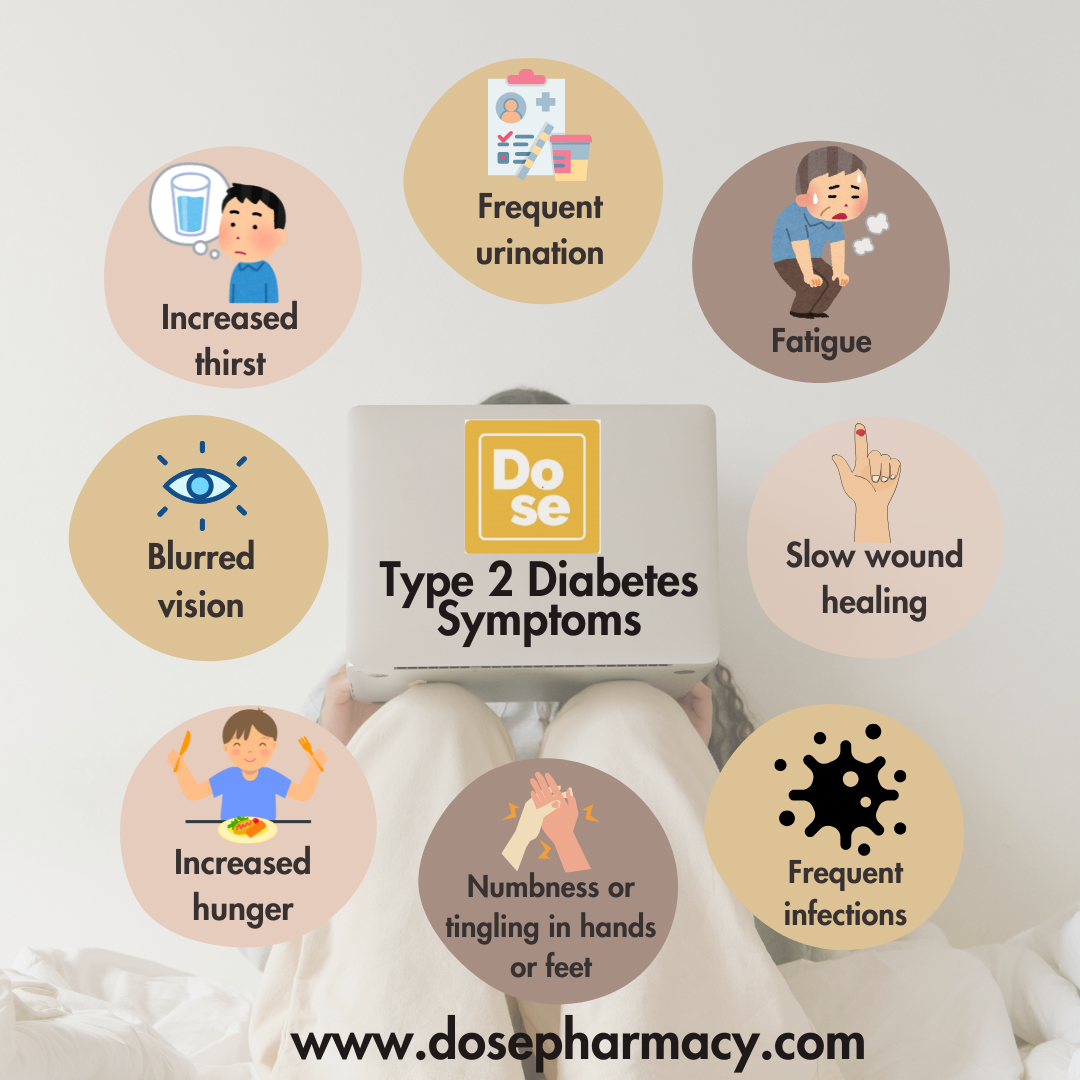
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes can develop gradually and may go unnoticed for a long time. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria) – High blood sugar levels force the kidneys to work harder to filter and remove excess glucose, leading to increased urination.
- Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia) – As a result of frequent urination, the body loses fluids, causing excessive thirst.
- Unexplained Weight Loss – Despite increased hunger, some individuals may experience weight loss due to the body breaking down fat and muscle for energy.
- Increased Hunger (Polyphagia) – The body’s inability to use glucose effectively can lead to persistent hunger.
- Fatigue and Weakness – High blood sugar levels can make it difficult for cells to access energy, causing fatigue.
- Blurred Vision – Excess glucose in the blood can cause swelling in the lens of the eye, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow-Healing Wounds – Poor circulation and high sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and fight infections.
- Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet – Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy) is a common complication of long-term uncontrolled diabetes.
- Darkened Skin Patches (Acanthosis Nigricans) – Some individuals develop dark, velvety skin patches in areas like the neck, armpits, and groin, which is a sign of insulin resistance.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
The exact cause of type 2 diabetes is complex and involves multiple factors, including genetics and lifestyle choices. Here are some primary causes:
- Insulin Resistance – In many cases, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin, forcing the pancreas to produce more. Over time, the pancreas struggles to keep up, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Genetic Predisposition – Family history plays a significant role. If one or both parents have type 2 diabetes, the risk of developing the condition increases.
- Obesity and Excess Body Fat – Being overweight, particularly with excess abdominal fat, increases insulin resistance, which is a major contributor to type 2 diabetes.
- Lack of Physical Activity – A sedentary lifestyle reduces the body’s ability to use glucose effectively, increasing the risk of diabetes.
- Poor Diet – A diet high in refined carbohydrates, sugary foods, and unhealthy fats contributes to insulin resistance and obesity.
- Hormonal Imbalances – Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, including:
- Age – The risk of type 2 diabetes increases after the age of 45, though it is becoming more common in younger people due to lifestyle changes.
- Family History – Having a parent or sibling with diabetes raises the risk significantly.
- Being Overweight or Obese – Excess fat, particularly around the abdomen, contributes to insulin resistance.
- Physical Inactivity – People who engage in less physical activity are more likely to develop diabetes.
- Unhealthy Eating Habits – A diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to obesity and insulin resistance.
- High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol – These conditions are often linked to diabetes and can contribute to the disease’s progression.
- Gestational Diabetes – Women who develop diabetes during pregnancy are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Ethnicity – Certain ethnic groups, including African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians, have a higher predisposition to developing type 2 diabetes.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption – Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase insulin resistance and contribute to diabetes development.
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
If you experience symptoms of type 2 diabetes, a doctor will perform several tests to confirm the diagnosis:
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test – Measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- A1C Test – Provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) – Measures blood sugar levels before and after consuming a glucose-rich drink.
- Random Blood Sugar Test – Measures blood sugar levels at any time of the day without fasting.
Prevention and Management
Although type 2 diabetes cannot always be prevented, lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk and help manage the condition effectively.
- Healthy Diet – Focus on whole foods, high-fiber vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats while reducing sugar and refined carbohydrates.
- Regular Exercise – Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Weight Management – Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce insulin resistance.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring – Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps in keeping diabetes under control.
- Medication – In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications like metformin to help manage blood sugar levels.
- Stress Management – Reducing stress through activities like meditation and yoga can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Complications of Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes
If left untreated, type 2 diabetes can lead to severe complications, including:
- Heart Disease – Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Kidney Disease – Damage to the kidneys, potentially leading to kidney failure.
- Nerve Damage – Diabetic neuropathy can cause pain and numbness, especially in the feet.
- Eye Problems – Diabetic retinopathy can lead to vision loss or blindness.
- Foot Problems – Poor circulation and nerve damage increase the risk of infections and amputations.
- Skin Infections – Increased risk of bacterial and fungal infections.
Type 2 diabetes is a serious yet manageable condition. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps toward prevention and early diagnosis. With proper lifestyle changes, medical supervision, and ongoing management, people with type 2 diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. If you suspect you have symptoms or are at risk, consult a healthcare professional for timely evaluation and guidance.
FAQs
1. What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes blood sugar (glucose). It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin to regulate glucose levels effectively.
2. What are the common symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
Symptoms may include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurry vision, slow-healing wounds, unexplained weight loss, and increased hunger.
3. What causes type 2 diabetes?
The main causes include insulin resistance, genetic factors, obesity, an unhealthy diet, and a sedentary lifestyle.
4. Who is at risk for developing type 2 diabetes?
People at higher risk include those who are overweight, have a family history of diabetes, lead an inactive lifestyle, or have high blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
5. Can type 2 diabetes be prevented?
Yes, adopting a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help lower the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
6. How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
Doctors use blood tests such as the fasting blood sugar test, A1C test, and oral glucose tolerance test to diagnose type 2 diabetes.
7. Is type 2 diabetes reversible?
While there is no permanent cure, some people can achieve remission through significant lifestyle changes, such as weight loss and improved diet.
8. What complications can arise from type 2 diabetes?
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, vision loss, and an increased risk of infections.
9. What foods should people with type 2 diabetes avoid?
Sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, processed foods, and excessive saturated fats should be limited to help manage blood sugar levels.
10. What is the best way to manage type 2 diabetes?
A combination of a balanced diet, regular physical activity, medication (if prescribed), and routine blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management.