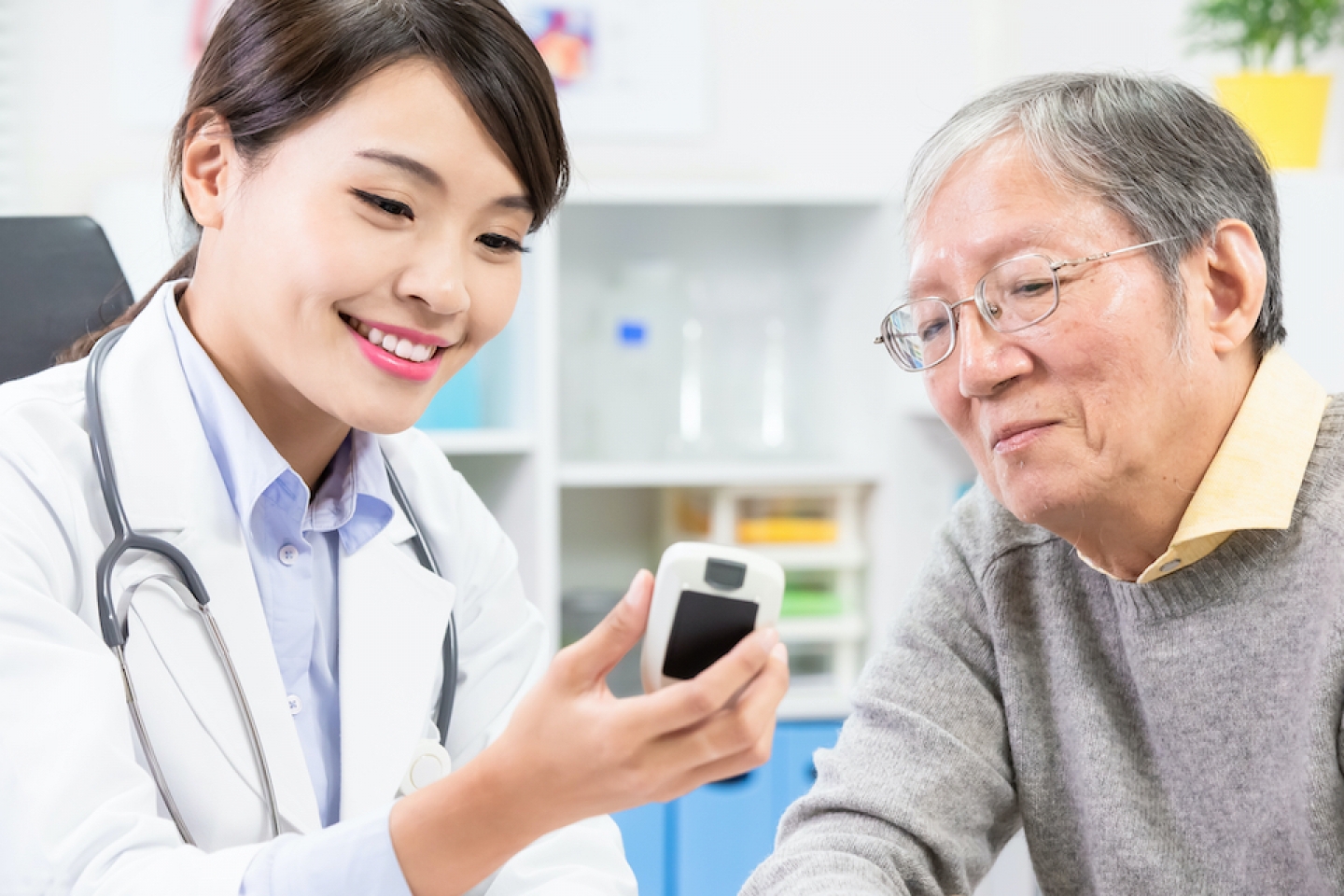
A chronic illness with high blood sugar that affects millions of individuals globally is diabetes. A comprehensive strategy that is adapted to each person’s needs, lifestyle, and health objectives is necessary for managing diabetes. In addition to controlling blood sugar levels, personalized diabetes care places a strong emphasis on general health and wellbeing. This article provides methods to improve quality of life and health by exploring important steps in personalized diabetes care.
Comprehending Diabetes
Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are the two main types that present. When the body is unable to manufacture insulin, a hormone essential for controlling blood sugar, type 1 diabetes develops. On the other hand, the body either stops producing enough insulin or becomes resistant to it, which is how Type 2 diabetes usually arises. Although there may be similarities in the management options for the two categories, each strategy should take age, lifestyle, and pre-existing medical issues into account.
First, form a comprehensive care team.
A caring and competent care team is the first step in creating a customized care plan.
This group could consist of:
Primary Care Physician:
In charge of managing issues associated to diabetes and keeping an eye on general health.
Endocrinologist:
An expert in hormone-related problems, such as insulin administration.
A registered dietitian can provide dietary advice to help control blood sugar levels.
A certified diabetes educator teaches patients how to take care of themselves, including how to check their blood sugar and take medications.
Mental health professionals deal with the psychological and emotional effects of diabetes.
Working with a multidisciplinary team guarantees that diabetes treatment is handled from all angles, enabling a more specialized strategy.
Step 2: Customized Dietary Schedules
A key component of managing diabetes is diet. It might not work to tackle nutrition in a one-size-fits-all manner. As an alternative, think about the following customized eating plans:
Counting Carbohydrates
It’s critical to comprehend how carbohydrates impact blood sugar. To become proficient at carb counting, consult a dietician. This technique can assist people in choosing foods that will regulate their blood sugar levels.
-
Knowledge of Glycemic Indices
Paying attention to a food’s glycemic index (GI) can be helpful. Low GI foods release glucose more gradually, assisting in the maintenance of stable blood sugar levels. A customized regimen may include low-GI foods including legumes, whole grains, and non-starchy veggies.
-
diabetes-patient-careThe Time and Frequency of Meals
Meal timing can be determined by lifestyle choices and preferences. Three well-balanced meals a day may help some people, while smaller, more frequent meals may help others control their blood sugar levels. Meal timing can be customized to decrease hunger and increase glycemic control.
-
Taking Cultural Preferences Into Account
Dietary programs ought to take cultural dietary customs into consideration. Work with a dietitian to develop a menu that satisfies dietary requirements while preserving a balanced diet.
Step 3: Individualized Exercise
Maintaining overall health and managing diabetes need regular physical activity. Personalized fitness regimens take into account each person’s preferences, current health issues, and level of fitness. The following are some tactics:
-
Look for Pleasurable Activities
Exercise doesn’t have to take place only at the gym. Investigate other choices, like biking, swimming, dancing, or walking. Engaging in enjoyable activities improves long-term success and adherence.
-
Make sensible objectives
Establish realistic exercise objectives based on your own abilities. These objectives could be as easy as progressively increasing physical activity or going for a ten-minute stroll each day. Reward minor accomplishments to keep yourself motivated.
-
Include Strength Training
Strength training helps control weight and increases insulin sensitivity. Make it a point to strength train your primary muscle groups for at least two days a week.
-
Keep an eye on your blood sugar levels
Recognize how various activities affect your blood sugar levels. Check your blood sugar levels before and after doing out so you can learn how to modify your diet and medication schedule.
Step 4: Monitoring Blood Sugar
For diabetes to be effectively managed, blood glucose levels must be regularly monitored. Personalized treatment ought to consist of:
-
Determining Monitoring Objectives
Establish goal blood sugar ranges after consulting medical professionals. Objectives could change depending on personal characteristics including age, health, and course of therapy.
-
Making Use of Technology
Real-time monitoring of blood sugar levels can be facilitated via smartphone apps and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs). Making better decisions is made possible by the information these technologies offer into the relationship between stress, exercise, and food and blood sugar levels.
-
Frequent Check-Ins
Make appointments for routine check-ins with medical professionals so you may talk about blood sugar readings and, if necessary, modify treatment strategies. This proactive strategy aids in pattern recognition and management strategy optimization.
Step 5: Handling Medication
Medication is a crucial part of treatment for many diabetics. Among the components of personalized medicine management are:
-
Being Aware of Drugs
Learn about the purpose, possible side effects, and interactions between prescribed medications and diet and other medications. Comprehending medication aids in maintaining effectiveness and adherence.
-
Consistent Evaluations
Review drug schedules with medical professionals on a regular basis to evaluate effectiveness and make any required modifications. Depending on their blood sugar patterns, weight, or lifestyle, some people might need to make adjustments.
-
Including Novel Treatments
Keep up with new developments in diabetes therapy and treatment. Investigating solutions like insulin pumps or novel oral drugs that suit specific needs may be part of personalized therapy.
Step 6: Emotional and Mental Health
Emotionally taxing diabetes management might result in feelings of annoyance, worry, or exhaustion. In order to address mental health, personalized care should:
Understanding Emotional Well-being Recognize the emotional effects of having diabetes. Assess yourself on a regular basis and note any overwhelm or stress you may be experiencing.
Seeking Support Look for a mental health expert who specializes in chronic illness, or consider joining a diabetes support group. Making connections with people going through comparable struggles can be a great source of emotional support.
Putting Stress Management and Mindfulness Into Practice
Incorporate mindfulness exercises to lower stress and improve mental clarity, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing techniques. Since stress can have a negative impact on blood sugar levels, stress management is essential.
Step 7: Routine Medical Examinations
One aspect of personalized diabetes patient care is continuing to be vigilant about being checked out. Frequent examinations should include:
-
Examinations of the feet and eyes
Regular foot inspections help avoid issues like ulcers or infections, while annual eye exams are necessary to detect diabetic retinopathy.
-
Measurements of cholesterol and blood pressure
Regularly check cholesterol and blood pressure levels to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, which is more common in people with diabetes.
-
Tests of Kidney Function
The condition of the kidneys is vital for diabetics. Frequent screenings can assist in identifying diabetic nephropathy early on.
Summary
A comprehensive strategy that takes into account each person’s particular needs, interests, and lifestyle is known as personalized care for diabetes. People with diabetes can dramatically enhance their health and well-being by creating a comprehensive care team, customizing diet and exercise regimens, controlling medication, monitoring blood sugar, attending to mental health issues, and guaranteeing routine screenings. Diabetes management can be difficult, but with the right strategy, people can successfully manage their illness and have happy, fulfilled lives. Accepting these actions encourages a better, healthier future by enabling people with diabetes to take control of their health.