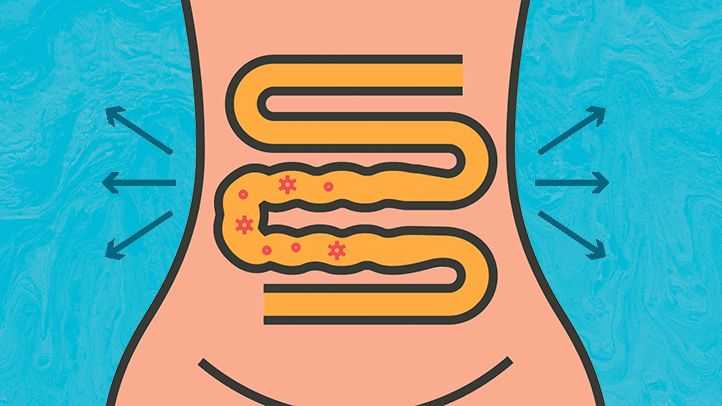
To reduce occurrences of loose bowel movements, adopting certain lifestyle changes can help maintain digestive health and prevent discomfort. This guide covers diet, hydration, hygiene practices, stress management, exercise, and appropriate medication use, including Nizonide 500mg, to address symptoms when necessary. Here’s an in-depth look at effective lifestyle adjustments
Diet Adjustments for Digestive Health
A balanced diet is fundamental in managing bowel movements. The foods we consume significantly impact our digestive processes, and specific dietary choices can reduce the frequency of diarrhea.
Increase Fiber Gradually
Foods high in fiber, such as oats, bananas, and whole grains, can aid in bowel regularity by absorbing excess water in the intestines. Soluble fiber is particularly effective in managing loose stools. However, sudden high-fiber intake can aggravate digestive symptoms, so increase fiber intake gradually.
Avoid Trigger Foods
Certain foods may act as triggers, causing loose bowel movements or irritating the digestive tract. These include spicy foods, caffeine, artificial sweeteners, and highly processed foods. Keeping a food diary can help identify individual triggers.
Include Probiotics
Probiotic-rich foods, like yogurt and fermented vegetables, support gut flora balance, which is essential for digestive health. Consuming probiotics regularly can strengthen the digestive system and reduce the likelihood of diarrhea.
Proper Hydration Practices
Dehydration is a common consequence of diarrhea, so maintaining hydration is essential for digestive health. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily and more when experiencing loose stools.
Use Electrolyte Solutions When Necessary
Replenishing lost electrolytes with solutions or beverages containing potassium, sodium, and magnesium can help prevent dehydration-related fatigue. In severe cases, consult a doctor about using electrolyte-replenishing drinks.
Avoid Sugary and Caffeinated Drinks
Sugary sodas and caffeinated beverages can worsen loose stools, as they increase bowel motility. Opt for water, herbal teas, and clear broths to stay hydrated without worsening symptoms.
Hygiene Practices to Prevent Infections
Hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing bacterial and parasitic infections, which often cause diarrhea.
Hand Washing
Proper handwashing before meals, after using the restroom, and after handling potentially contaminated items can help prevent the spread of infection-causing bacteria and parasites.
Food Safety
Ensure all foods are properly cooked and stored. Avoid consuming undercooked meat, unpasteurized dairy products, and raw seafood, which can carry harmful pathogens.
Filtered Water
In areas where water quality is questionable, drink filtered or boiled water to prevent infection-related diarrhea.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can disrupt digestive health, leading to symptoms like diarrhea and bloating. Learning to manage stress effectively may reduce occurrences of loose stools.
Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can reduce stress levels, which may positively impact gut health.
Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is beneficial not only for physical health but also for managing stress. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week to maintain a healthy mind-gut connection.
Incorporate Physical Activity
Regular physical activity promotes a healthy digestive system and reduces the risk of gastrointestinal issues.
Moderate Aerobic Exercise
Activities like walking, jogging, and cycling help stimulate digestive function and reduce stress, both of which play roles in preventing diarrhea.
Avoid Intense Exercise After Eating
Strenuous exercise immediately after eating can disrupt digestion and increase the likelihood of loose stools, so allow your body some time to digest food before engaging in vigorous workouts.
Use of Medications When Needed
Sometimes, medication is required to treat underlying infections or specific digestive issues causing loose bowel movements.
Nizonide 500mg as Treatment for Protozoal Infections
If loose stools result from parasitic infections such as giardiasis or cryptosporidiosis, nizonide 500mg, containing nitazoxanide, may be prescribed. This antiparasitic medication works by inhibiting the growth of parasites responsible for diarrhea, effectively alleviating symptoms. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider before starting Nizonide to ensure appropriate usage and dosage, as it is not intended for long-term or preventive use.
Antidiarrheal Medications for Symptomatic Relief
Over-the-counter options like loperamide may provide short-term relief from diarrhea symptoms, but they should not be used for extended periods without medical advice. If symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional.
Monitor for Food Intolerances or Sensitivities
Certain food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity, can contribute to loose bowel movements. Identifying and managing these sensitivities can help alleviate symptoms.
Lactose Intolerance
People with lactose intolerance may experience diarrhea after consuming dairy products. Opt for lactose-free alternatives or use lactase supplements if necessary.
Gluten Sensitivity or Celiac Disease
Those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease must avoid gluten-containing foods, as consuming them can lead to diarrhea and other gastrointestinal issues.
Maintain a Consistent Meal Schedule
Eating at regular intervals can promote a more stable digestive system. Erratic eating patterns may disrupt the natural rhythm of digestion and contribute to loose stools.
Avoid Large Meals
Large meals can strain the digestive system, so try eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This approach also helps regulate blood sugar and energy levels.
Mindful Eating
Chewing food thoroughly and eating slowly can improve digestion by allowing digestive enzymes to work effectively. Mindful eating also prevents overeating, which may lead to digestive discomfort.
Monitor Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, including antibiotics and some types of laxatives, can disrupt gut flora and lead to diarrhea. Consult your doctor if you suspect any medication may be causing loose bowel movements.
Antibiotic Usage
Antibiotics can disturb the balance of gut bacteria, often causing diarrhea. To help restore gut flora, consider probiotics or consult your doctor about preventive measures if you’re prescribed antibiotics.
Avoid Overuse of Laxatives
Laxatives should only be used when necessary, as overuse can impair normal bowel function and cause diarrhea.
Track Symptoms and Seek Medical Guidance
Maintaining a symptom diary can help identify patterns and potential causes of diarrhea. Record details such as food intake, stress levels, medication usage, and bowel movement consistency. This information can be useful when consulting a healthcare provider, especially if diarrhea persists.
When facing persistent diarrhea, particularly if it’s accompanied by symptoms like abdominal pain, fever, or dehydration, seek medical advice. Medications like Nizonide 500mg may be prescribed if a protozoal infection is identified as the cause, but self-diagnosis should be avoided.
Conclusion
Implementing these lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of loose bowel movements. A balanced diet, adequate hydration, good hygiene practices, stress management, regular exercise, and mindful eating all contribute to a healthier digestive system. Additionally, when symptoms are due to parasitic infections, medications like Nizonide 500mg may offer relief, but they should only be used under medical supervision. Through these practices, individuals can achieve improved digestive health and greater overall well-being.